HTTP API(REST API)
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
- HTTP 메시지 바디의 데이터를 InputStream을 사용해서 직접 읽을 수 있다.
먼저
1. 단순한 텍스트 메시지를 HTTP 메시지 바디에 담아서 전송하고 읽어 본 후
2. JSON 형식으로 전송하고 읽어 보자.
1. 단순 TEXT 전송
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyStringServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-string")
public class RequestBodyStringServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// inputStream으로 메시지바디의 데이터를 바이트코드로 바로 얻을 수 있다.
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
// 항상 바이트 <--> 문자로 변환할 때는 인코딩을 지정해 주어야 한다.
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 출력
System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody);
response.getWriter().write("OK");
}
}
postman을 이용하여 TEXT를 전송해 보자. (post -> body -> raw- > Text -> Send)

결과

-> messageBody에 TEXT형식의 데이터가 담겨있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
정리
POST http://localhost:8080/request-body-string
content-type: text/plain
message body: hello.
2. JSON 형식 전송
JSON 형식으로 파싱할 수 있게 객체를 하나 생성한다. (lombok을 사용했다.)
@Getter @Setter
public class HelloData {
private String username;
private int age;
}JSON 결과를 파싱해서 사용할 수 있는 자바 객체로 변환하려면
Jackson, Gson 같은 JSON 변환 라이브러리를 추가해서 사용해야 한다.
Spring Boot로 Spring MVC를 선택하면 기본으로 Jackson 라이브러리( ObjectMapper )를 함께 제공한다.
@WebServlet(name = "requestBodyJsonServlet", urlPatterns = "/request-body-json")
public class RequestBodyJsonServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// inputStream으로 메시지바디의 데이터를 바이트코드로 바로 얻을 수 있다.
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
// 항상 바이트 <--> 문자로 변환할 때는 어떤 인코딩 지정해야 한다.
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 출력
System.out.println("messageBody = " + messageBody);
// 파싱 작업
// messageBody에 담긴 Json형식의 데이터를 HelloData로 파싱한다.
HelloData helloData = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody, HelloData.class);
System.out.println("helloData.getUsername = " + helloData.getUsername());
System.out.println("helloData.getAge = " + helloData.getAge());
response.getWriter().write("OK");
}
}
postman을 이용하여 JSON형식으로 전송해 보자. (post -> body -> raw- > JSON -> Send)

결과
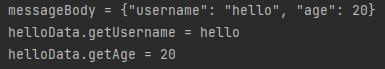
-> messageBody에 JSON형식의 데이터가 담겨있는 것을 확인할 수 있고
helloData 객체에 데이터가 정상적으로 파싱까지 된것까지 확인할 수 있다.
정리
POST http://localhost:8080/request-body-json
content-type: application/json
message body: {"username": "hello", "age": 20}
결과: messageBody = {"username": "hello", "age": 20}
Reference
https://www.inflearn.com/course/%EC%8A%A4%ED%94%84%EB%A7%81-mvc-1/
'HTTP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [HTTP] HTTP 상태코드 (0) | 2021.11.22 |
|---|---|
| [HTTP] 인터넷 네트워크(IP, TCP, UDP, DNS) (0) | 2021.08.09 |
| [HTTP] 데이터 요청 - POST (0) | 2021.07.25 |
| [HTTP] 데이터 요청 - GET (0) | 2021.07.25 |
| [HTTP] HTTP 데이터 요청 3가지 (0) | 2021.07.24 |